Step-by-step guide
Overview of the approach to obtain high quality population genomes from multiple deep metagenomes using differential coverage as the primary binning method.
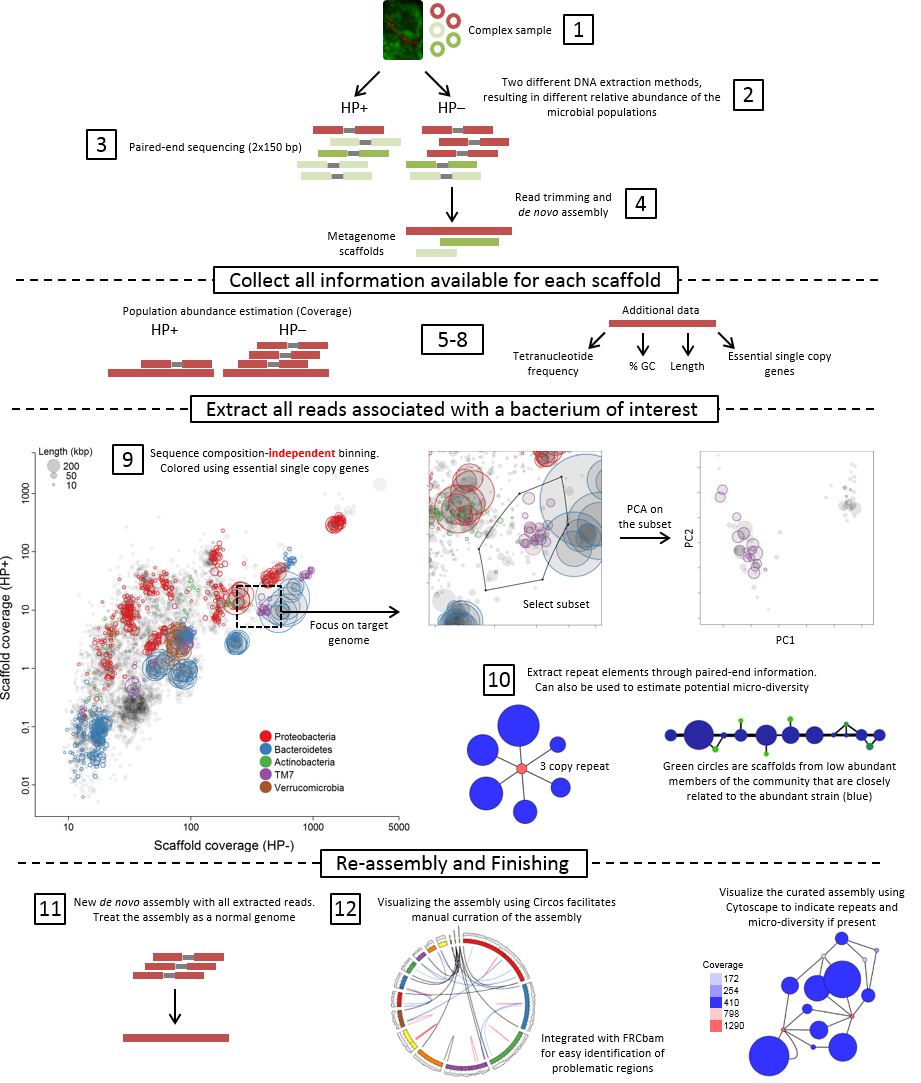
Samples, sequencing and assembly
At least two different samples are needed, which contians the target organisms in different abundances (step 1+2). Each sample is then independently shotgun-sequenced followed by a combined de novo assembly (step 3+4).
Collect all information available for each scaffold
In step 5-8 all data is prepared for subsequent analyis in R. The main focus of the approach is data integration, which allow informed choices in the binning process. Differential coverage is calculated by independently mapping the reads from each metagenome to the de novo assembled scaffolds, hence generating two abundance estimates (coverages) per scaffold.
Extract all reads associated with a bacterium of interest
Binning (clustering) of scaffolds into population genomes is done by plotting the two coverage estimates (one from each metagenome) against each other for all scaffolds using Rstudio (step 9). Scaffold subsets clustering together represents putative population genomes and are extracted as initial bins. As multiple species can be present in the same coverage-defined subset, the selected scaffold subset is further refined using principle component analysis of tetranucleotide frequencies. All data is integrated in R, thereby enabling the use of essential and single copy genes directly in the binning process.
As some genes are present in multiple copies (e.g. 16S rRNA or transposases) they will not be included in the initial coverage-defined subset. Instead paired-end read information is used to associate multiple copy genes with the appropriate genome bin (step 10).
Reassembly and finishing
All reads associated with a genome bin of interest are extracted and re-assembled using parameters optimised for each genome as the bins now can be treated as standard single genomes (step 11). Population genome assemblies are validated through analysis of conserved single copy genes, and through Circos in which all relevant assembly metrics are integrated to identify mis-assemblies and other structural problems (step 12).
All data generation and integration is automated and can be carried out using a FastA file of the assembled scaffolds and SAM files of the read mappings to the scaffolds.