Wrighton data re-analysis
This small guide show the R part of the extraction of five OD1 genomes from the dataset generated by Wrighton et al., 2012 and re-analysed by Albertsen et al., 2013.
The R markdown version of the guide can be found here as wrighton.workflow.Rmd.
The raw metagenome reads were obtained from SRA and de novo assembled as described in Albertsen et al., 2013.
Download the R formatted data.
Download and upack the Wrighton data used in Albertsen et al., 2013.
download.file('https://dl.dropbox.com/s/irahp88uleuqzv6/wrighton.tar.gz','wrighton.tar.gz', method = 'wget')
untar('wrighton.tar.gz')
Load needed packages
In case you havn’t installed all the needed packages, they can be installed via e.g. install.packages('vegan'). The version of R used to generate this file was:
R.version$version.string
"R version 3.0.1 (2013-05-16)"
library("vegan")
library("plyr")
library("RColorBrewer")
library("alphahull")
library("ggplot2")
Load files associated with the Albertsen de novo assembly of the Wrighton data
All data except the three coverage estimates (artur, dolly and chris) was generated from a fasta file of the assembled scaffolds (assembly.fa) using the script: workflow.R.data.generation.sh. Coverage estimates for the scaffolds was obtained through CLC’s short read mapper.
artur <- read.csv("assembly/artur.csv", header = T)
dolly <- read.csv("assembly/dolly.csv", header = T)
chris <- read.csv("assembly/chris.csv", header = T)
gc <- read.delim("assembly/assembly.gc.tab", header = T)
kmer <- read.delim("assembly/assembly.kmer.tab", header = T)
ess <- read.table("assembly/assembly.orfs.hmm.id.txt", header = F)
ess.tax <- read.delim("assembly/assembly.orfs.hmm.blast.tax.tab", header = F)
cons.tax <- read.delim("assembly/assembly.tax.consensus.txt", header = T)
colnames(kmer)[1] = "name"
colnames(ess) = c("name", "orf", "hmm.id")
colnames(ess.tax) = c("name", "orf", "phylum")
colnames(cons.tax) = c("name", "phylum", "tax.color", "all.assignments")
Merge all data on scaffolds into a single data frame d.
d <- as.data.frame(cbind(artur$Name, artur$Reference.length, gc$gc, artur$Average.coverage, dolly$Average.coverage, chris$Average.coverage), row.names = F)
colnames(d) = c("name", "length", "gc", "artur", "dolly", "chris")
d <- merge(d, cons.tax, by = "name", all = T)
Merge all data on essential genes into a single data frame e.
e <- merge(ess, d, by = "name", all.x = T)
e <- merge(e, ess.tax, by = c("name", "orf"), all.x = T)
Load the original de novo assembly by Wrighton and the associated bins
I added the data as a simple single text file in the org.wrigton folder. The assembled sequences and original bins were obtained from here.
w.d <- read.delim("org.wrighton/acd.genomes.txt", header = T)
Define a few functions for later use
Calculate basic statistics on a set of scaffolds.
genome.stats <- matrix(NA, nrow = 0, ncol = 10)
colnames(genome.stats) <- c("total.length", "# scaffolds", "mean.length", "max.length", "gc", "artur", "dolly", "chris", "tot.ess", "uni.ess")
calc.genome.stats <- function(x, y) matrix(c(sum(x$length), nrow(x), round(mean(x$length), 1), max(x$length), round(sum((x$gc * x$length))/sum(x$length), 1), round(sum((x$artur * x$length))/sum(x$length), 1), round(sum((x$dolly * x$length))/sum(x$length), 1), round(sum((x$chris * x$length))/sum(x$length), 1), nrow(y), length(unique(y$hmm.id))), dimnames = list(colnames(genome.stats), ""))
Extract a subset of scaffolds.
extract <- function(x, a.def, v1, v2) {
out <- {}
for (i in 1:nrow(x)) {
if (inahull(a.def, c(v1[i], v2[i])))
out <- rbind(out, x[i, ])
}
return(out)
}
GC color scheme.
rgb.c <- colorRampPalette(c("red", "green", "blue"))
rgb.a <- adjustcolor(rgb.c(max(d$gc) - min(d$gc)), alpha.f = 0.5)
Initial overview of the data
calc.genome.stats(d, e)
total.length 171324044.0
# scaffolds 62199.0
mean.length 2754.5
max.length 220980.0
gc 43.5
artur 14.7
dolly 15.0
chris 17.5
tot.ess 5800.0
uni.ess 108.0
To get an initial overview of the data we only use scaffolds > 5000 bp.
ds <- subset(d, length > 5000)
es <- subset(e, length > 5000)
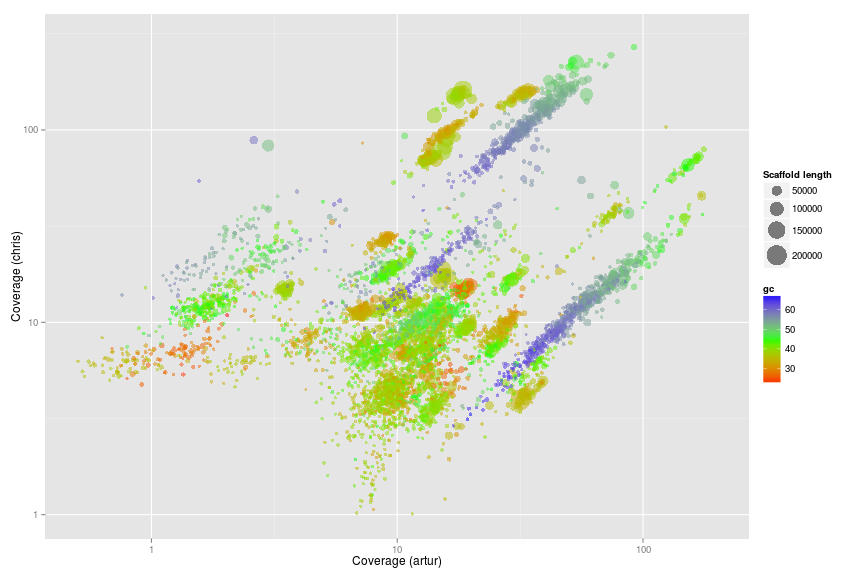
Coverage plots - Colored by GC
ggplot(ds, aes(x = artur, y = chris, color = gc, size = length)) +
scale_x_log10(limits = c(0.5, 200)) +
scale_y_log10(limits = c(1, 300)) +
xlab("Coverage (artur)") +
ylab("Coverage (chris)") +
geom_point(alpha = 0.5) +
scale_size_area(name = "Scaffold length", max_size = 10) +
scale_colour_gradientn(colours = c("red", "green", "blue"))
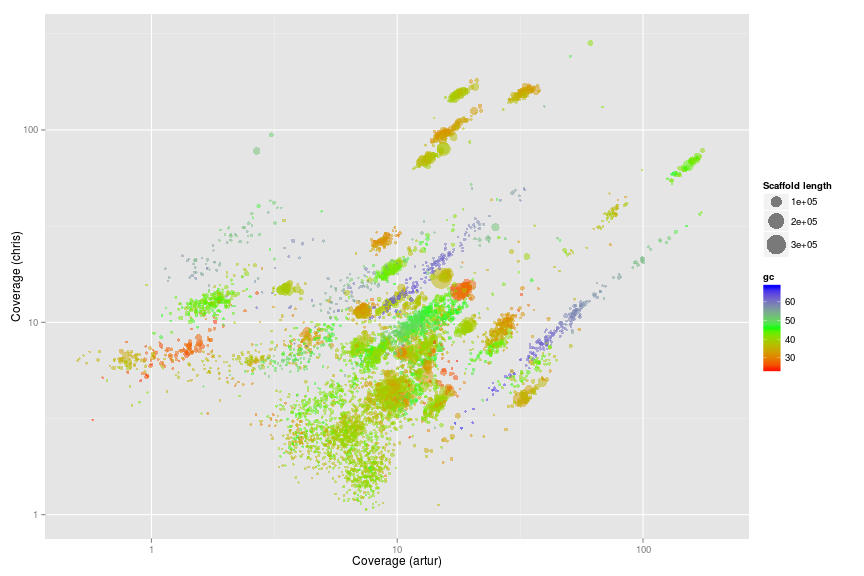
Original Wrighton coverage plots - Colored by GC
w.ds <- subset(w.d, length > 5000)
ggplot(w.ds, aes(x = artur, y = chris, color = gc, size = length)) +
scale_x_log10(limits = c(0.5, 200)) +
scale_y_log10(limits = c(1, 300)) +
xlab("Coverage (artur)") +
ylab("Coverage (chris)") +
geom_point(alpha = 0.5) +
scale_size_area(name = "Scaffold length", max_size = 10) +
scale_colour_gradientn(colours = c("red", "green", "blue"))
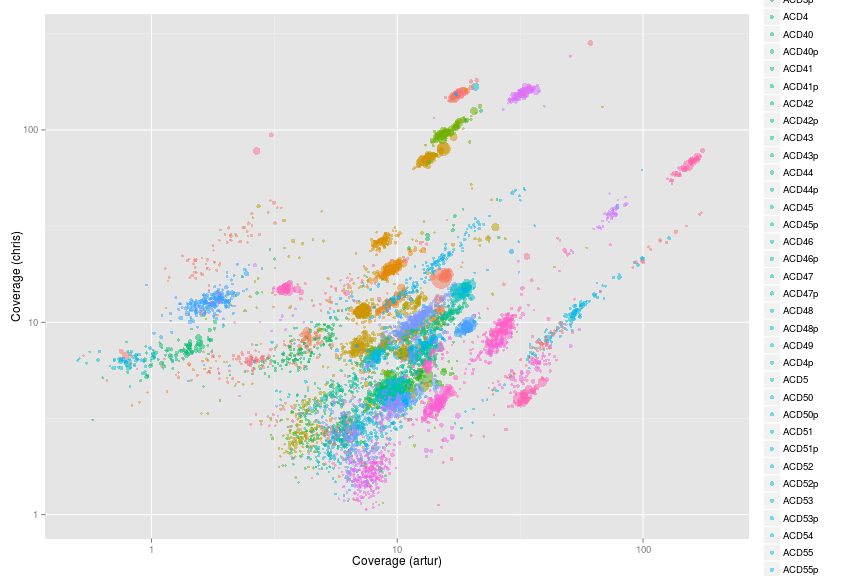
Original Wrighton coverage plots - Colored by bins
ggplot(w.ds, aes(x = artur, y = chris, color = bin, size = length)) +
scale_x_log10(limits = c(0.5, 200)) +
scale_y_log10(limits = c(1, 300)) +
xlab("Coverage (artur)") +
ylab("Coverage (chris)") +
geom_point(alpha = 0.5) +
scale_size_area(name = "Scaffold length", max_size = 10)
Looking at the 5 orginal OD1 bins from Wrighton
w.d.od1 <- subset(w.d, bin == "ACD7" | bin == "ACD11" | bin == "ACD18" | bin == "ACD81" | bin == "ACD1")
ggplot(w.d.od1, aes(x = artur, y = dolly, color = bin, size = length)) +
scale_x_log10(limits = c(0.5, 200)) +
scale_y_log10(limits = c(1, 300)) +
xlab("Coverage (artur)") +
ylab("Coverage (chris)") +
geom_point(alpha = 0.5) +
scale_size_area(name = "Scaffold length", max_size = 10)
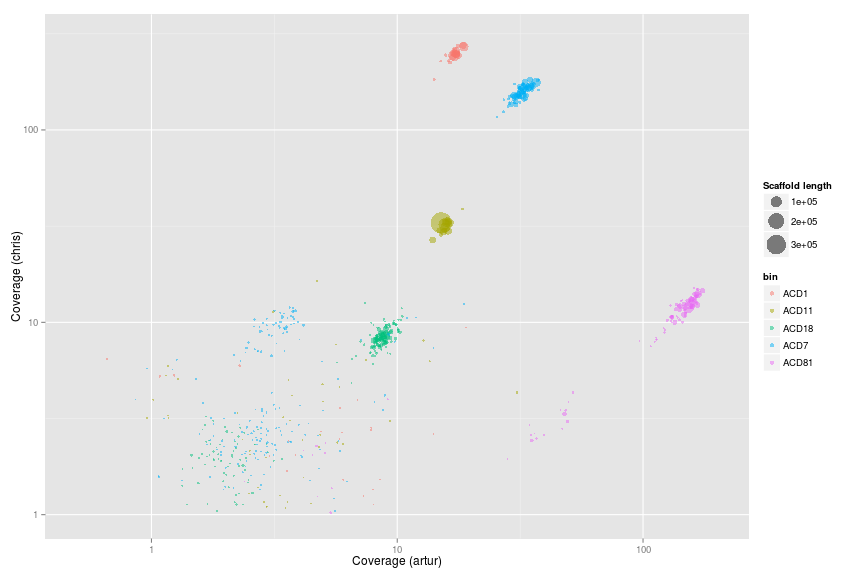
Genome extraction
ACD7 (ID1)
palette(rgb.a)
x <- "artur"
y <- "dolly"
plot(d[, x], d[, y], log = "xy", cex = sqrt(d$length)/100, pch = 20, col = d$gc - min(d$gc), xlim = c(10, 110), ylim = c(110, 330), xlab = "artur", ylab = "dolly")
# def<-locator(100, type='p', pch=20)
def <- {}
def$x <- c(22.53, 29.37, 43.54, 41.99, 32.09, 22.00, 21.65)
def$y <- c(158.24, 198.66, 196.48, 147.04, 112.07, 111.66, 125.12)
selection.A <- ahull(def, alpha = 1e+05)
plot(selection.A, col = "black", add = T)
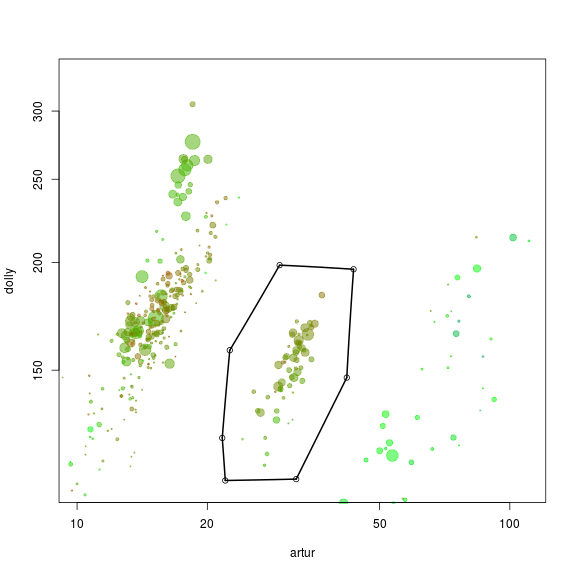
Extract all scaffolds and information on essential genes within the defined subspace using the extract function.
s.A <- extract(d, selection.A, d[, x], d[, y])
e.A <- extract(e, selection.A, e[, x], e[, y])
See the basic statistics of the selected scaffolds.
calc.genome.stats(s.A, e.A)
total.length 1411386.0
# scaffolds 59.0
mean.length 23921.8
max.length 110546.0
gc 34.9
artur 31.6
dolly 154.2
chris 151.4
tot.ess 96.0
uni.ess 96.0
Add the genome statistics to a list and print the name of the scaffolds to a file for further refinement.
genome.stats <- rbind(genome.stats, t(calc.genome.stats(s.A, e.A)))
rownames(genome.stats)[nrow(genome.stats)] <- "ACD7"
show(genome.stats)
total.length # scaffolds mean.length max.length gc artur dolly chris tot.ess uni.ess
ACD7 1411386 59 23922 110546 34.9 31.6 154.2 151.4 96 96
write.table(g1.s.A$name, file = "ACD7.txt", quote = F, row.names = F, col.names = F)
The name of the scaffolds can be used to extract the scaffolds from the original assembly.fa.
ACD11 (ID7)
palette(rgb.a)
x <- "artur"
y <- "chris"
plot(d[, x], d[, y], log = "xy", cex = sqrt(d$length)/100, pch = 20, col = d$gc - min(d$gc), xlim = c(14, 20), ylim = c(12, 24), xlab = "Coverage (artur)", ylab = "Coverage (chris)")
# def<-locator(100, type='p', pch=20)
def <- {}
def$x <- c(14.49, 15.44, 16.40, 16.43, 15.84, 14.88, 14.18, 14.29)
def$y <- c(18.89, 19.86, 18.51, 16.86, 16.37, 15.91, 16.21, 17.35)
selection.A <- ahull(def, alpha = 1e+05)
plot(selection.A, col = "black", add = T)
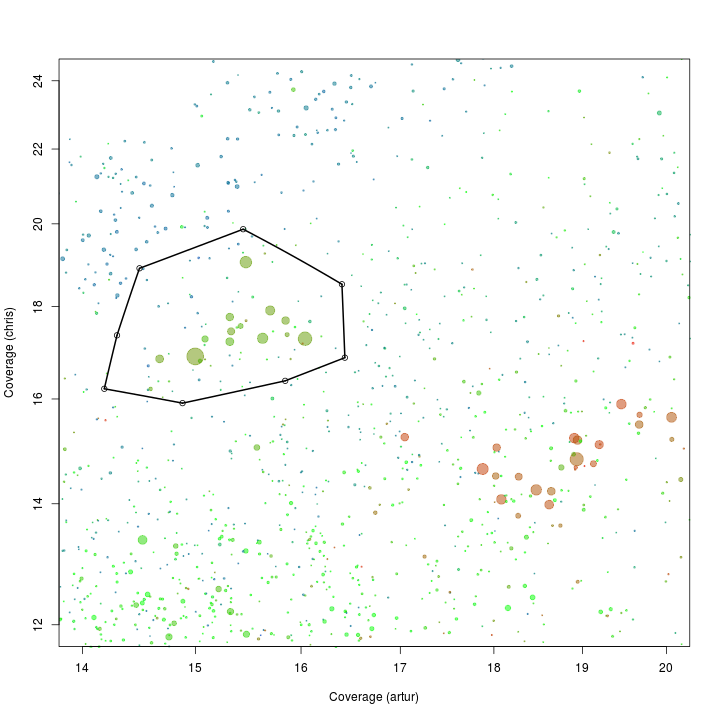
Extract all scaffolds and information on essential genes within the defined subspace using the extract function.
s.A <- extract(d, selection.A, d[, x], d[, y])
e.A <- extract(e, selection.A, e[, x], e[, y])
See the basic statistics of the selected scaffolds.
calc.genome.stats(s.A, e.A)
total.length 1074415.0
# scaffolds 76.0
mean.length 14137.0
max.length 220980.0
gc 38.5
artur 15.4
dolly 29.0
chris 17.5
tot.ess 97.0
uni.ess 91.0
Which of the single copy genes are duplicated? Note that some genomes might have duplicates of some “single copy genes”.
d.A <- e.A[which(duplicated(e.A$hmm.id) | duplicated(e.A$hmm.id, fromLast = TRUE)), ]
d.A[order(d.A$hmm.id), c(1, 3, 9)]
name hmm.id phylum.x
713 1361 PF00750.14 <NA>
4584 536 PF00750.14 Firmicutes
5264 735 PF00750.14 Firmicutes
1897 22123 TIGR01009 Proteobacteria
2928 3244 TIGR01009 Firmicutes
1898 22123 TIGR01044 Proteobacteria
2927 3244 TIGR01044 Firmicutes
1899 22123 TIGR01050 Proteobacteria
2926 3244 TIGR01050 Firmicutes
5261 735 TIGR02012 Firmicutes
5284 7436 TIGR02012 <NA>
As there is multiple genomes in the subset we make a PCA on the scaffolds in the subset.
rda <- rda(kmer[s.A$name, 2:ncol(kmer)], scale = T)
scores <- scores(rda, choices = 1:5)$sites
s.B <- cbind(s.A, scores)
e.B <- merge(e.A, s.B[, c(1, 9:13)], all.x = T, by = "name")
d.B <- merge(d.A, s.B[, c(1, 9:13)], all.x = T, by = "name")
We use the pairs function to plot the first 3 components along with GC and coverages.
palette(rgb.a)
pairs(s.B[, c(4, 5, 6, 3, 10:12)], upper.panel = NULL, col = s.B$gc - min(d$gc), cex = sqrt(s.B$length)/100, pch = 20)
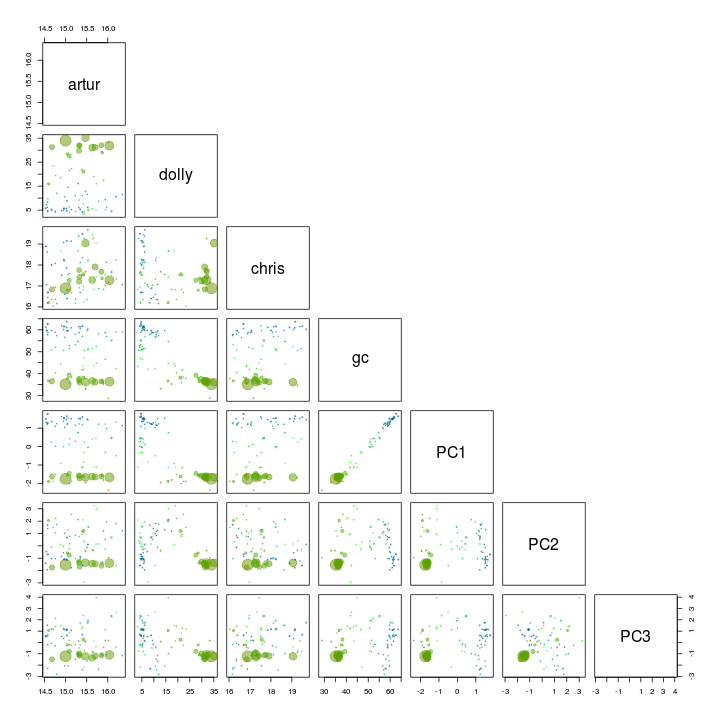
GC and PC1 seem to seperate our target genome from the other scaffolds and is therefore used for another extraction using the locator function.
palette(rgb.a)
x <- "PC1"
y <- "gc"
plot(s.B[, x], s.B[, y], cex = sqrt(s.B$length)/100, pch = 20, col = s.B$gc - min(d$gc), xlab = x, ylab = y)
palette(brewer.pal(9, "Set1"))
points(s.B[, x], s.B[, y], col = s.B$tax.color + 1, pch = 20)
# def<-locator(100, type='p', pch=20)
def <- {}
def$x <- c(-2.24, -1.92, -1.32, -1.11, -1.35, -1.91, -2.21)
def$y <- c(36.54, 41.04, 41.34, 38.59, 33.38, 30.21, 30.93)
selection.B <- ahull(def, alpha = 1e+05)
plot(selection.B, col = "black", add = T)
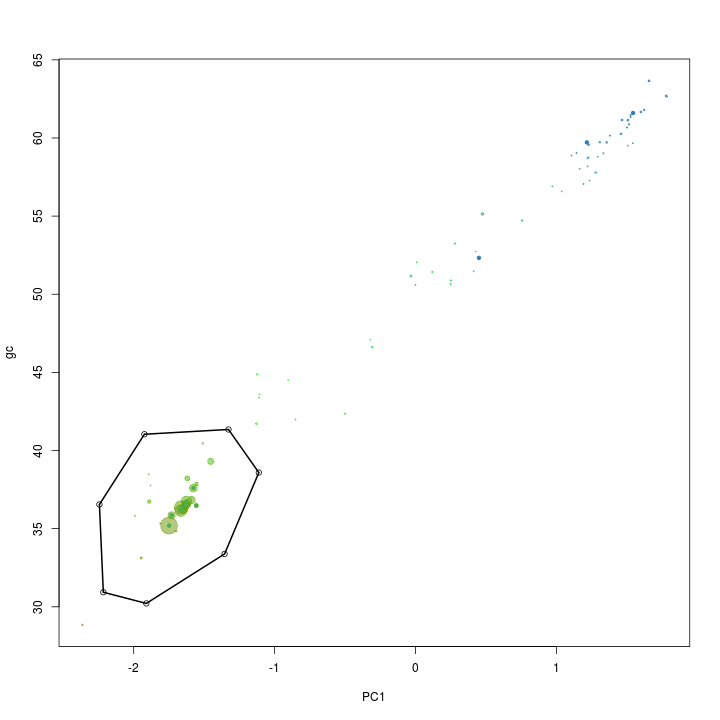
Again the extract function is used to retrive the scaffolds in the selected subset.
s.C <- extract(s.B, selection.B, s.B[, x], s.B[, y])
e.C <- extract(e.B, selection.B, e.B[, x], e.B[, y])
See the basic statistics of the selected scaffolds.
calc.genome.stats(s.C, e.C)
total.length 955434.0
# scaffolds 22.0
mean.length 43428.8
max.length 220980.0
gc 36.3
artur 15.4
dolly 31.7
chris 17.4
tot.ess 91.0
uni.ess 89.0
There are a few duplicated “single copy genes” however in this case it is not due to mulitple species in the bin, but real duplicates in the genome.
d.C <- e.C[which(duplicated(e.C$hmm.id) | duplicated(e.C$hmm.id, fromLast = TRUE)), ]
d.C[order(d.C$hmm.id), c(1, 3, 9)]
name hmm.id phylum.x
4 536 PF00750.14 Firmicutes
21 735 PF00750.14 Firmicutes
28 1361 PF00750.14 <NA>
Add the genome statistics to a list and print the name of the scaffolds to a file for further refinement.
genome.stats <- rbind(genome.stats, t(calc.genome.stats(s.C, e.C)))
rownames(genome.stats)[nrow(genome.stats)] <- "ACD11"
show(genome.stats)
total.length # scaffolds mean.length max.length gc artur dolly chris tot.ess uni.ess
ACD7 1411386 59 23922 110546 34.9 31.6 154.2 151.4 96 96
ACD11 955434 22 43429 220980 36.3 15.4 31.7 17.4 91 89
write.table(s.C$name, file = "ACD11.txt", quote = F, row.names = F, col.names = F)
ACD18 (ID3)
palette(rgb.a)
x <- "artur"
y <- "chris"
plot(d[, x], d[, y], log = "xy", cex = sqrt(d$length)/100, pch = 20, col = d$gc - min(d$gc), xlim = c(5, 15), ylim = c(20, 35), xlab = "Coverage (artur)", ylab = "Coverage (chris)")
# def<-locator(100, type='p', pch=20)
def <- {}
def$x <- c(7.12, 7.75, 8.80, 10.54, 10.91, 10.97, 9.70, 8.65, 7.66, 6.81, 6.96)
def$y <- c(26.89, 28.41, 30.11, 29.28, 27.47, 25.55, 24.59, 23.85, 22.95, 23.46, 25.60)
selection.A <- ahull(def, alpha = 1e+05)
plot(selection.A, col = "black", add = T)
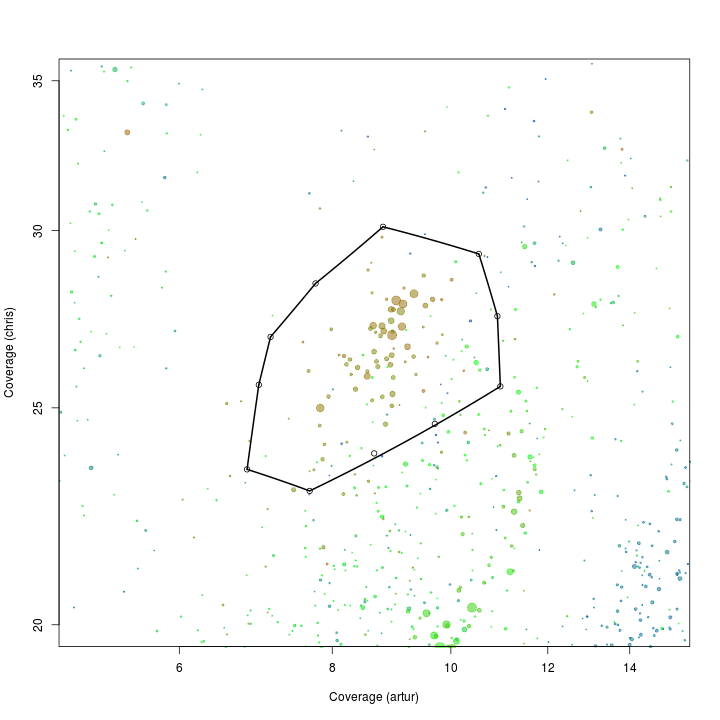
Extract all scaffolds and information on essential genes within the defined subspace using the extract function.
s.A <- extract(d, selection.A, d[, x], d[, y])
e.A <- extract(e, selection.A, e[, x], e[, y])
See the basic statistics of the selected scaffolds.
calc.genome.stats(s.A, e.A)
total.length 1230983.0
# scaffolds 110.0
mean.length 11190.8
max.length 65437.0
gc 34.0
artur 8.9
dolly 8.6
chris 26.7
tot.ess 92.0
uni.ess 86.0
Which of the single copy genes are duplicated? Note that some genomes might have duplicates of some “single copy genes”.
d.A <- e.A[which(duplicated(e.A$hmm.id) | duplicated(e.A$hmm.id, fromLast = TRUE)), ]
d.A[order(d.A$hmm.id), c(1, 3, 9)]
name hmm.id phylum.x
3795 43010 PF00297.17 Proteobacteria
4944 5995 PF00297.17 Firmicutes
4285 49498 PF00411.14 <NA>
4615 540 PF00411.14 Firmicutes
4286 49498 PF00416.17 <NA>
4617 540 PF00416.17 Firmicutes
3796 43010 PF00573.17 Proteobacteria
4942 5995 PF00573.17 Firmicutes
607 13098 TIGR00436 <NA>
5431 8080 TIGR00436 Firmicutes
4613 540 TIGR02027 Firmicutes
5630 9043 TIGR02027 Proteobacteria
As there is multiple genomes in the subset we make a PCA on the scaffolds in the subset.
rda <- rda(kmer[s.A$name, 2:ncol(kmer)], scale = T)
scores <- scores(rda, choices = 1:5)$sites
s.B <- cbind(s.A, scores)
e.B <- merge(e.A, s.B[, c(1, 9:13)], all.x = T, by = "name")
d.B <- merge(d.A, s.B[, c(1, 9:13)], all.x = T, by = "name")
We use the pairs function to plot the first 5 components. I’ve also added GC and coverage.
palette(rgb.a)
pairs(s.B[, c(4, 5, 6, 3, 10:12)], upper.panel = NULL, col = s.B$gc - min(d$gc), cex = sqrt(s.B$length)/100, pch = 20)
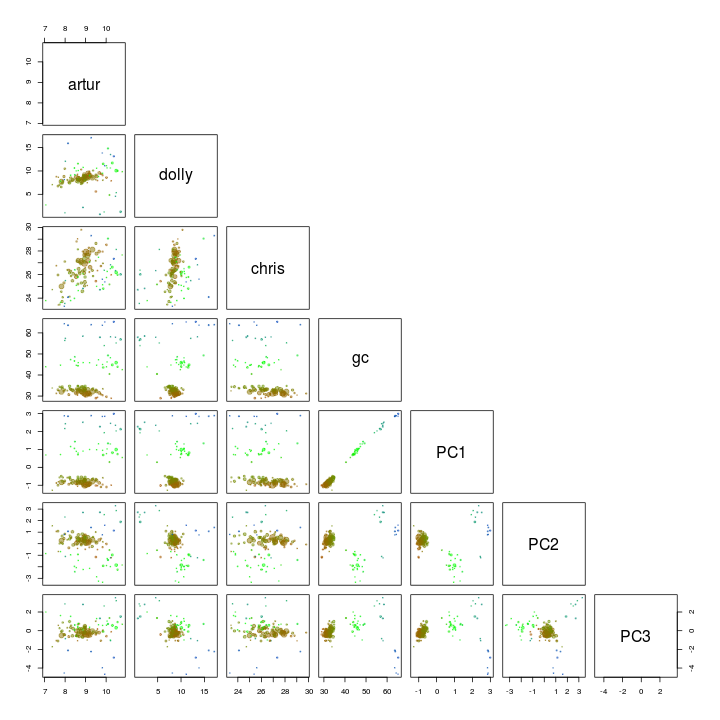
PC1 and PC2 seem to seperate our target genome from the other scaffolds and is therefore used for another extraction using the locator function.
palette(rgb.a)
x <- "PC1"
y <- "PC2"
plot(s.B[, x], s.B[, y], cex = sqrt(s.B$length)/100, pch = 20, col = s.B$gc - min(d$gc), xlab = x, ylab = y)
palette(brewer.pal(9, "Set1"))
points(s.B[, x], s.B[, y], col = s.B$tax.color + 1, pch = 20)
# def<-locator(100, type='p', pch=20)
def <- {}
def$x <- c(-1.39, -0.89, -0.27, -0.44, -1.12, -1.40)
def$y <- c(1.75, 1.93, 0.80, -2.00, -2.27, -0.54)
selection.B <- ahull(def, alpha = 1e+05)
plot(selection.B, col = "black", add = T)
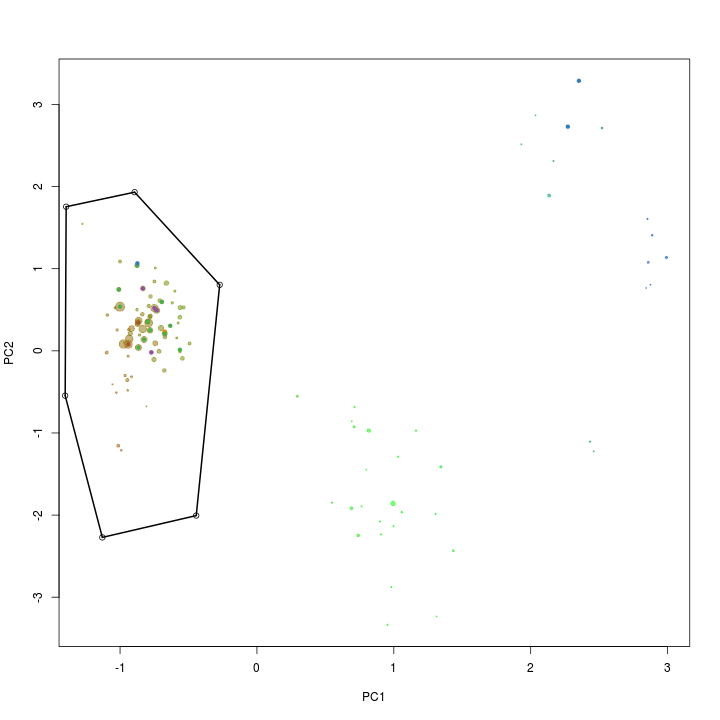
Again the extract function is used to retrive the scaffolds in the selected subset.
s.C <- extract(s.B, selection.B, s.B[, x], s.B[, y])
e.C <- extract(e.B, selection.B, e.B[, x], e.B[, y])
See the basic statistics of the selected scaffolds.
calc.genome.stats(s.C, e.C)
total.length 1110432.0
# scaffolds 72.0
mean.length 15422.7
max.length 65437.0
gc 32.3
artur 8.8
dolly 8.5
chris 26.7
tot.ess 86.0
uni.ess 85.0
There are a few duplicated “single copy genes” however in this case it is not due to mulitple species in the bin, but real duplicates in the genome.
d.C <- e.C[which(duplicated(e.C$hmm.id) | duplicated(e.C$hmm.id, fromLast = TRUE)), ]
d.C[order(d.C$hmm.id), c(1, 3, 9)]
name hmm.id phylum.x
73 8080 TIGR00436 Firmicutes
80 13098 TIGR00436 <NA>
Add the genome statistics to a list and print the name of the scaffolds to a file for further refinement.
genome.stats <- rbind(genome.stats, t(calc.genome.stats(s.C, e.C)))
rownames(genome.stats)[nrow(genome.stats)] <- "ACD18"
show(genome.stats)
total.length # scaffolds mean.length max.length gc artur dolly chris tot.ess uni.ess
ACD7 1411386 59 23922 110546 34.9 31.6 154.2 151.4 96 96
ACD11 955434 22 43429 220980 36.3 15.4 31.7 17.4 91 89
ACD18 1110432 72 15423 65437 32.3 8.8 8.5 26.7 86 85
write.table(s.C$name, file = "ACD18.txt", quote = F, row.names = F, col.names = F)
ACD81 (ID16)
palette(rgb.a)
x <- "artur"
y <- "chris"
plot(d[, x], d[, y], log = "xy", cex = sqrt(d$length)/100, pch = 20, col = d$gc - min(d$gc), xlim = c(50, 400), ylim = c(20, 100), xlab = "Coverage (artur)", ylab = "Coverage (chris)")
# def<-locator(100, type='p', pch=20)
def <- {}
def$x <- c(141.32, 182.22, 220.68, 206.56, 154.17, 115.47, 91.13, 106.59)
def$y <- c(77.13, 89.70, 82.59, 66.62, 52.24, 42.95, 47.99, 59.07)
selection.A <- ahull(def, alpha = 1e+05)
plot(selection.A, col = "black", add = T)
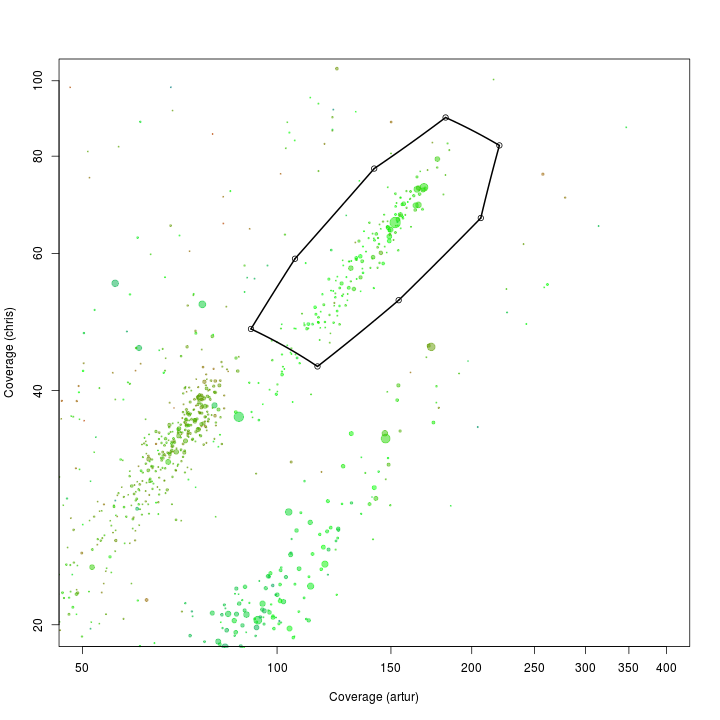
Extract all scaffolds and information on essential genes within the defined subspace using the extract function.
s.A <- extract(d, selection.A, d[, x], d[, y])
e.A <- extract(e, selection.A, e[, x], e[, y])
See the basic statistics of the selected scaffolds.
calc.genome.stats(s.A, e.A)
##
## total.length 835481.0
## # scaffolds 161.0
## mean.length 5189.3
## max.length 85982.0
## gc 43.3
## artur 147.5
## dolly 12.4
## chris 63.8
## tot.ess 76.0
## uni.ess 74.0
Which of the single copy genes are duplicated? Note that some genomes might have duplicates of some “single copy genes”.
d.A <- e.A[which(duplicated(e.A$hmm.id) | duplicated(e.A$hmm.id, fromLast = TRUE)), ]
d.A[order(d.A$hmm.id), c(1, 3, 9)]
name hmm.id phylum.x
3170 3520 TIGR00442 Firmicutes
5429 802 TIGR00442 <NA>
5231 7191 TIGR00981 Firmicutes
5482 828 TIGR00981 <NA>
As there is multiple genomes in the subset we make a PCA on the scaffolds in the subset.
rda <- rda(kmer[s.A$name, 2:ncol(kmer)], scale = T)
scores <- scores(rda, choices = 1:5)$sites
s.B <- cbind(s.A, scores)
e.B <- merge(e.A, s.B[, c(1, 9:13)], all.x = T, by = "name")
d.B <- merge(d.A, s.B[, c(1, 9:13)], all.x = T, by = "name")
We use the pairs function to plot the first 3 components. I’ve also added GC and coverage.
palette(rgb.a)
pairs(s.B[, c(4, 5, 6, 3, 10:12)], upper.panel = NULL, col = s.B$gc - min(d$gc), cex = sqrt(s.B$length)/100, pch = 20)
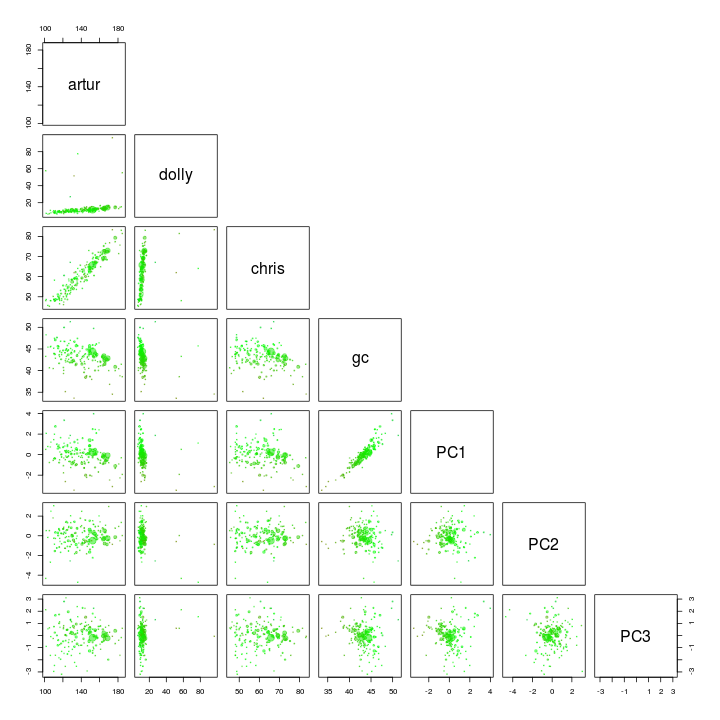
Dolly and PC1 seem to seperate our target genome from the other scaffolds and is therefore used for another extraction using the locator function.
palette(rgb.a)
x <- "dolly"
y <- "PC1"
plot(s.B[, x], s.B[, y], cex = sqrt(s.B$length)/100, pch = 20, col = s.B$gc - min(d$gc), xlab = x, ylab = y)
palette(brewer.pal(9, "Set1"))
points(s.B[, x], s.B[, y], col = s.B$tax.color + 1, pch = 20)
# def<-locator(100, type='p', pch=20)
def <- {}
def$x <- c(4.70, 10.45, 21.96, 25.94, 19.75, 6.91, 4.26, 3.48)
def$y <- c(3.08, 4.14, 3.67, 0.09, -2.74, -3.08, -0.75, 1.24)
selection.B <- ahull(def, alpha = 1e+05)
plot(selection.B, col = "black", add = T)
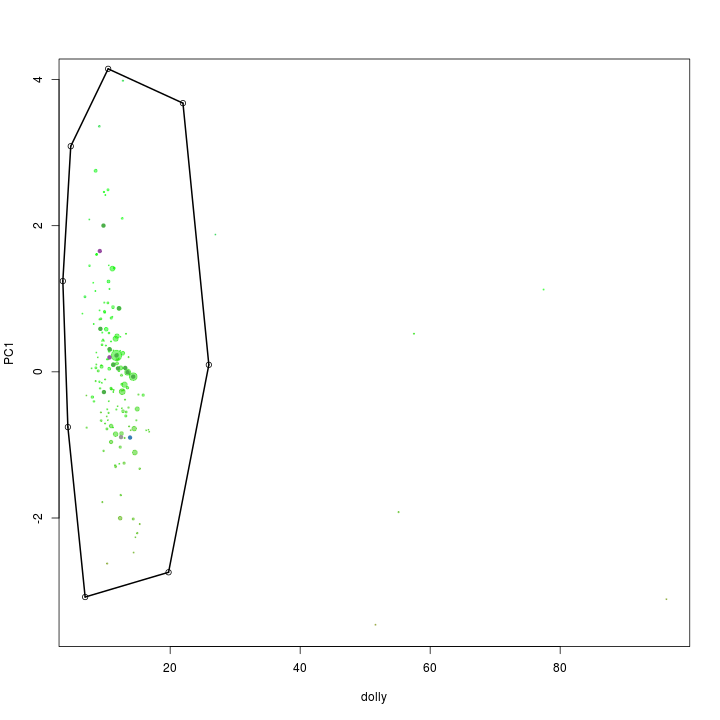
Again the extract function is used to retrive the scaffolds in the selected subset.
s.C <- extract(s.B, selection.B, s.B[, x], s.B[, y])
e.C <- extract(e.B, selection.B, e.B[, x], e.B[, y])
See the basic statistics of the selected scaffolds.
calc.genome.stats(s.C, e.C)
total.length 826830.0
# scaffolds 155.0
mean.length 5334.4
max.length 85982.0
gc 43.4
artur 147.6
dolly 11.9
chris 63.7
tot.ess 76.0
uni.ess 74.0
There are a few duplicated “single copy genes”. In this case it might indicate that the bin includes a small amount of another bacteria. It can be cleaned up by using the cytoscape network graph approach.
d.C <- e.C[which(duplicated(e.C$hmm.id) | duplicated(e.C$hmm.id, fromLast = TRUE)), ]
d.C[order(d.C$hmm.id), c(1, 3, 9)]
name hmm.id phylum.x
53 802 TIGR00442 <NA>
67 3520 TIGR00442 Firmicutes
56 828 TIGR00981 <NA>
75 7191 TIGR00981 Firmicutes
Add the genome statistics to a list and print the name of the scaffolds to a file for further refinement.
genome.stats <- rbind(genome.stats, t(calc.genome.stats(s.C, e.C)))
rownames(genome.stats)[nrow(genome.stats)] <- "ACD81"
show(genome.stats)
total.length # scaffolds mean.length max.length gc artur dolly chris tot.ess uni.ess
ACD7 1411386 59 23922 110546 34.9 31.6 154.2 151.4 96 96
ACD11 955434 22 43429 220980 36.3 15.4 31.7 17.4 91 89
ACD18 1110432 72 15423 65437 32.3 8.8 8.5 26.7 86 85
ACD81 826830 155 5334 85982 43.4 147.6 11.9 63.7 76 74
write.table(s.C$name, file = "ACD81.txt", quote = F, row.names = F, col.names = F)
ACD1 (ID2)
palette(rgb.a)
x <- "artur"
y <- "chris"
plot(d[, x], d[, y], log = "xy", cex = sqrt(d$length)/100, pch = 20, col = d$gc - min(d$gc), xlim = c(10, 40), ylim = c(50, 200), xlab = "Coverage (artur)", ylab = "Coverage (chris)")
# def<-locator(100, type='p', pch=20)
def <- {}
def$x <- c(13.56, 18.23, 22.18, 20.97, 14.47, 12.58)
def$y <- c(137.01, 183.62, 163.20, 139.54, 111.12, 113.64)
selection.A <- ahull(def, alpha = 1e+05)
plot(selection.A, col = "black", add = T)
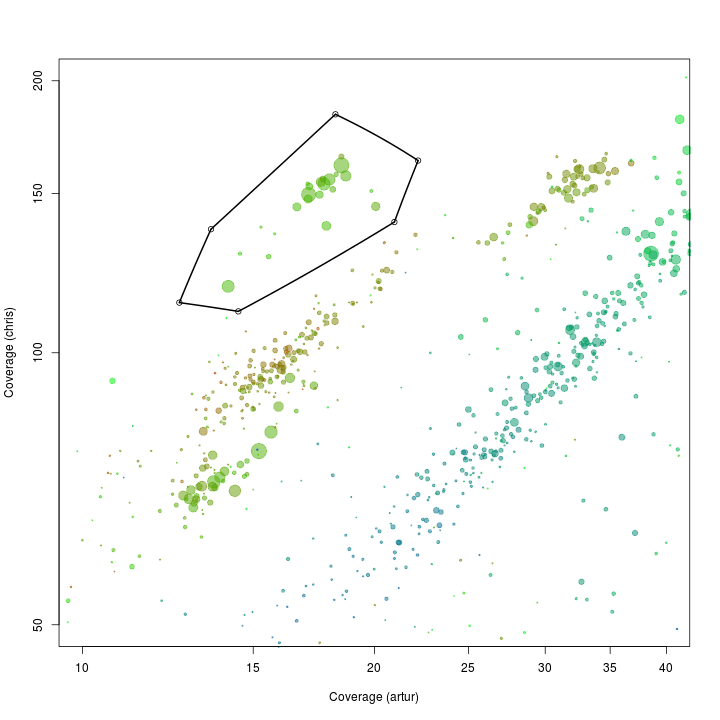
Extract all scaffolds and information on essential genes within the defined subspace using the extract function.
s.A <- extract(d, selection.A, d[, x], d[, y])
e.A <- extract(e, selection.A, e[, x], e[, y])
See the basic statistics of the selected scaffolds.
calc.genome.stats(s.A, e.A)
total.length 1269939.0
# scaffolds 23.0
mean.length 55214.7
max.length 176667.0
gc 38.3
artur 17.5
dolly 249.1
chris 149.2
tot.ess 97.0
uni.ess 94.0
Which of the single copy genes are duplicated? Note that some genomes might have duplicates of some “single copy genes”.
d.A <- e.A[which(duplicated(e.A$hmm.id) | duplicated(e.A$hmm.id, fromLast = TRUE)), ]
d.A[order(d.A$hmm.id), c(1, 3, 9)]
name hmm.id phylum.x
2316 2608 PF00750.14 Firmicutes
4299 4971 PF00750.14 Firmicutes
943 1510 TIGR00029 Firmicutes
2390 270 TIGR00029 <NA>
357 119 TIGR00442 Firmicutes
1685 2054 TIGR00442 Firmicutes
As there is multiple genomes in the subset we make a PCA on the scaffolds in the subset.
rda <- rda(kmer[s.A$name, 2:ncol(kmer)], scale = T)
scores <- scores(rda, choices = 1:5)$sites
s.B <- cbind(s.A, scores)
e.B <- merge(e.A, s.B[, c(1, 9:13)], all.x = T, by = "name")
d.B <- merge(d.A, s.B[, c(1, 9:13)], all.x = T, by = "name")
We use the pairs function to plot the first 3 components. I’ve also added GC and coverage. There is nothing obiouvs that can be removed.
palette(rgb.a)
pairs(s.B[, c(4, 5, 6, 3, 10:12)], upper.panel = NULL, col = s.B$gc - min(d$gc), cex = sqrt(s.B$length)/100, pch = 20)
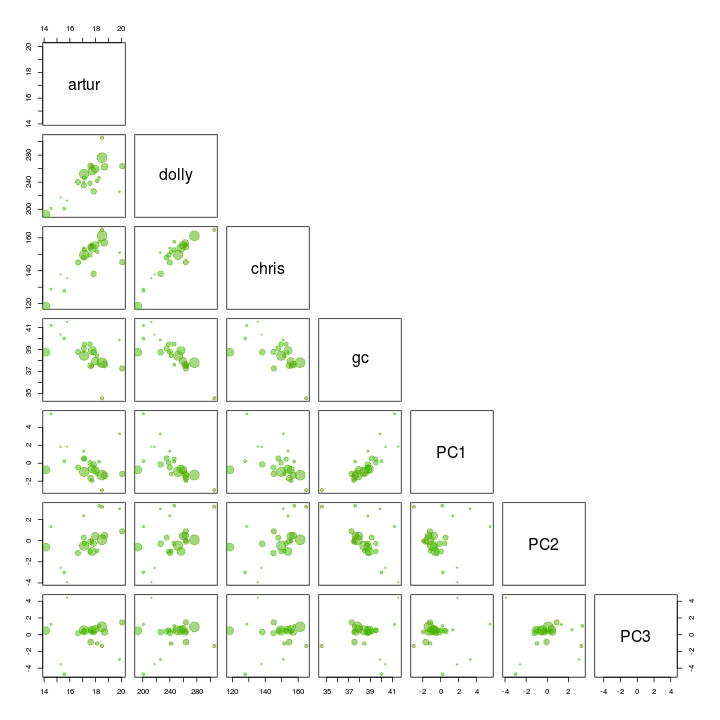
Add the genome statistics to a list and print the name of the scaffolds to a file for further refinement.
genome.stats <- rbind(genome.stats, t(calc.genome.stats(s.B, e.B)))
rownames(genome.stats)[nrow(genome.stats)] <- "ACD1"
show(genome.stats)
total.length # scaffolds mean.length max.length gc artur dolly chris tot.ess uni.ess
ACD7 1411386 59 23922 110546 34.9 31.6 154.2 151.4 96 96
ACD11 955434 22 43429 220980 36.3 15.4 31.7 17.4 91 89
ACD18 1110432 72 15423 65437 32.3 8.8 8.5 26.7 86 85
ACD81 826830 155 5334 85982 43.4 147.6 11.9 63.7 76 74
ACD1 1269939 23 55215 176667 38.3 17.5 249.1 149.2 97 94
write.table(s.B$name, file = "ACD1.txt", quote = F, row.names = F, col.names = F)